HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It refers to the systems used to control the temperature, humidity, and air quality in buildings. An HVAC system is a complete home comfort system that can heat, cool, and ventilate indoor spaces, providing improved indoor air quality and humidity control.
Key Components of an HVAC System
- Central Heating Unit: This includes furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps that provide warmth during colder months.
- Cooling Unit: Air conditioners and heat pumps are used to lower indoor temperatures and remove excess humidity.
- Ventilation Components: Ductwork, air handlers, vents, and registers are essential for circulating air efficiently throughout the building.
- Ancillary Devices: Thermostats, air filters, humidifiers, and dehumidifiers enhance performance and control over indoor conditions.
How HVAC Systems Work?
- Heating: Furnaces and boilers generate heat, which is distributed through ductwork or other methods. Heat pumps can extract heat from various sources and transfer it indoors.
- Cooling: Air conditioners and heat pumps absorb heat from the indoor environment and release it outdoors. Refrigerant cycles through the system to cool the air.
- Ventilation: Mechanical and natural ventilation methods are used to exchange or replace air in spaces, controlling temperature, humidity, and air quality.
What are the main components of an HVAC system?
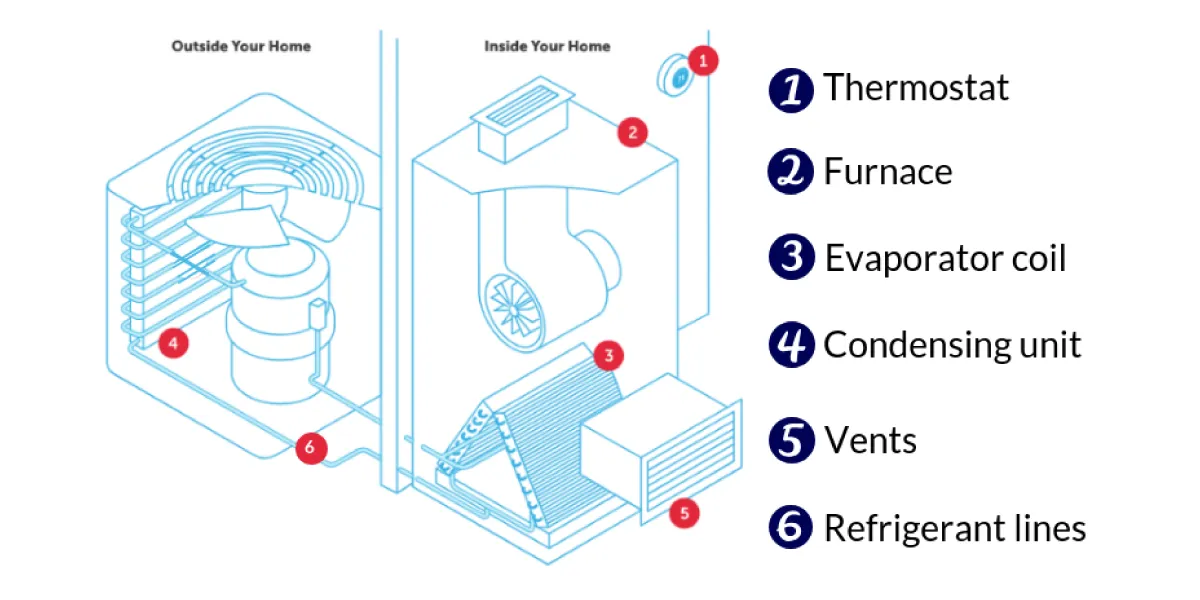
An HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system is composed of several key components that work together to regulate indoor temperature, humidity, and air quality. The main components include:
Central Heating Unit:
Provides heat by warming air and distributing it through ductwork. It can be fueled by natural gas, electricity, or oil. Absorbs heat from combustion and transfers it to cold air, which is then circulated through the building.
Cooling Unit:
Lowers indoor temperatures and removes excess humidity by absorbing heat from the indoor environment and releasing it outdoors: Can reverse its operation to provide both heating and cooling by circulating refrigerant through coils.
Ventilation Components:
A network of channels that transport conditioned air throughout the building. It includes supply ducts for distributing conditioned air and return ducts for pulling air back to the air conditioner or furnace.
Houses the blower and other mechanisms that aid in air circulation, pushing air through the ducts and into various parts of the building. Entry and exit points for air in each room, equipped with adjustable louvers to control airflow direction and volume.
Ancillary Devices:
The control center of the HVAC system, allowing users to set and adjust indoor temperatures.
Converts liquid refrigerant to gas, absorbing heat and cooling the air. It is part of the cooling process, located indoors. Located outside, it includes a compressor, condenser coil, and fan. It cools and condenses refrigerant, releasing heat into the outdoor air. Carry refrigerant between the indoor evaporator coil and the outdoor condenser unit, playing a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle.
Powers a fan to push warm or cool air through the ductwork and into the building.
Air Filters: Critical for maintaining air quality by filtering out impurities.
These components work together to maintain a comfortable indoor environment, enhance energy efficiency, and improve overall indoor living conditions.
How does an HVAC system improve indoor air quality?

HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems play a crucial role in maintaining good indoor air quality (IAQ) by controlling various factors that affect the air inside buildings. Here are the key ways an HVAC system improves indoor air quality:
1. Efficient Ventilation
Dilution of Pollutants: HVAC systems ensure a continuous flow of fresh outdoor air into indoor spaces, diluting indoor pollutants and preventing the buildup of harmful substances.
Air Exchange: Regular exchange of indoor and outdoor air helps reduce indoor air pollutants, promoting healthier indoor environments.
2. Humidity Control
Preventing Mold and Mildew: By maintaining appropriate humidity levels (between 30% and 50%), HVAC systems prevent the growth of mold and mildew, which can release spores into the air.
Comfort and Health: Balanced humidity levels are essential for both comfort and health, reducing the risk of mold growth and associated health issues.
3. Air Filtration
Removing Particulates: HVAC systems come equipped with air filters that capture and eliminate contaminants such as dust, pollen, bacteria, and viruses from the air, ensuring cleaner air circulation.
High-Efficiency Filters: Upgrading to high-efficiency filters (e.g., MERV 13 or 14) can diminish indoor air pollution by up to 99%, significantly improving air quality.
4. Whole-Home Air Purification
Enhanced Allergen Removal: Whole-home air purifiers can reduce allergens, germs, and odors, creating a healthier and more comfortable living environment.
Comprehensive Air Quality Improvement: These systems work in tandem with HVAC systems to ensure that circulated air is free from harmful pollutants.
5. Regular Maintenance
Filter Replacement: Regularly changing air filters (every 1-3 months) is crucial for maintaining efficient air filtration and preventing the accumulation of contaminants.
Duct Cleaning: Periodic duct cleaning helps remove dust, debris, and potential mold growth from ductwork, ensuring clean and uncontaminated air flow.
6. Smart Thermostats and Energy Efficiency
Precise Control: Smart thermostats provide precise control over temperature and humidity levels, enhancing both comfort and indoor air quality.
Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient HVAC systems (e.g., Energy Star rated) contribute to better indoor air quality by operating effectively and conserving energy
How does ductwork affect the efficiency of an HVAC system?

Ductwork plays a crucial role in the efficiency of an HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system. The design, installation, and condition of ductwork significantly impact the overall performance and energy efficiency of the system.
Key Factors Affecting Ductwork Efficiency
Duct Size and Layout:
Proper Sizing: Ducts should be appropriately sized to ensure the right amount of air reaches each room. Undersized ducts can cause high resistance to airflow, leading to increased energy consumption, while oversized ducts can result in reduced airflow and inefficiency.
Layout: A well-planned, straighter layout minimizes resistance and helps maintain efficiency. Excessive twists and turns can restrict airflow, making the HVAC system work harder.
Air Leaks and Insulation:
Air Leaks: Leaks in ductwork can lead to significant energy loss as conditioned air escapes before reaching its intended destination. Sealing leaks is critical to prevent these losses.
Insulation: Properly insulating ducts, especially in unconditioned spaces, is essential to prevent heat transfer and reduce energy consumption.
Balanced Airflow:
Airflow Dynamics: Balanced airflow is vital for the system to perform at its best. Properly sized and laid out ducts help maintain consistent airflow throughout all areas of the building.
Return Air Placement: The strategic placement of return air vents ensures that the HVAC system pulls in air from the right sources, preventing it from working harder to reach the desired temperature.
Material Selection:
The choice of duct material affects airflow efficiency. Smooth interior surfaces, like those found in metal ducts, minimize resistance to airflow compared to flexible ducts.
Regular Maintenance:
Inspections and Repairs: Regular inspections can identify issues such as leaks, obstructions, or damage that restrict airflow. Simple repairs, like sealing leaks and checking insulation, can significantly improve ductwork efficiency.
Conclusion
Efficient ductwork is essential for maximizing HVAC system performance and energy efficiency. Proper design, installation, and maintenance of ductwork can significantly reduce energy consumption, improve comfort levels, and extend the lifespan of the HVAC system. By understanding the importance of ductwork and taking steps to ensure its optimal performance, homeowners and building managers can create more comfortable and energy-efficient environments.
HVAC systems are crucial for maintaining comfortable indoor environments. Understanding the various components and how they work together helps in maintaining and optimizing these systems for efficient performance and energy savings.